Want To Know More About Our Company?
Curious What Else We Do?
Wecruit Pte Ltd (“Wecruit”) was incorporated with the idea that employment is an intimate process of human interaction.
How to Become a Chartered Accountant in Singapore + Salary List
The main pathway to becoming a Chartered Accountant of Singapore, also known as CA (Singapore), is through the Singapore Chartered Accountant Qualification (SCAQ), administered by the Singapore Accountancy Commission (SAC).
The key steps include:
1. Meeting the Academic Requirement: A recognised degree in accountancy or equivalent.
2. Completing the SCAQ Programme: Includes foundation, professional, and capstone modules.
3. Fulfilling Practical Experience: At least three years of relevant work experience.
4. Registering as a Chartered Accountant of Singapore: After meeting all requirements, individuals can apply for the CA (Singapore) designation.
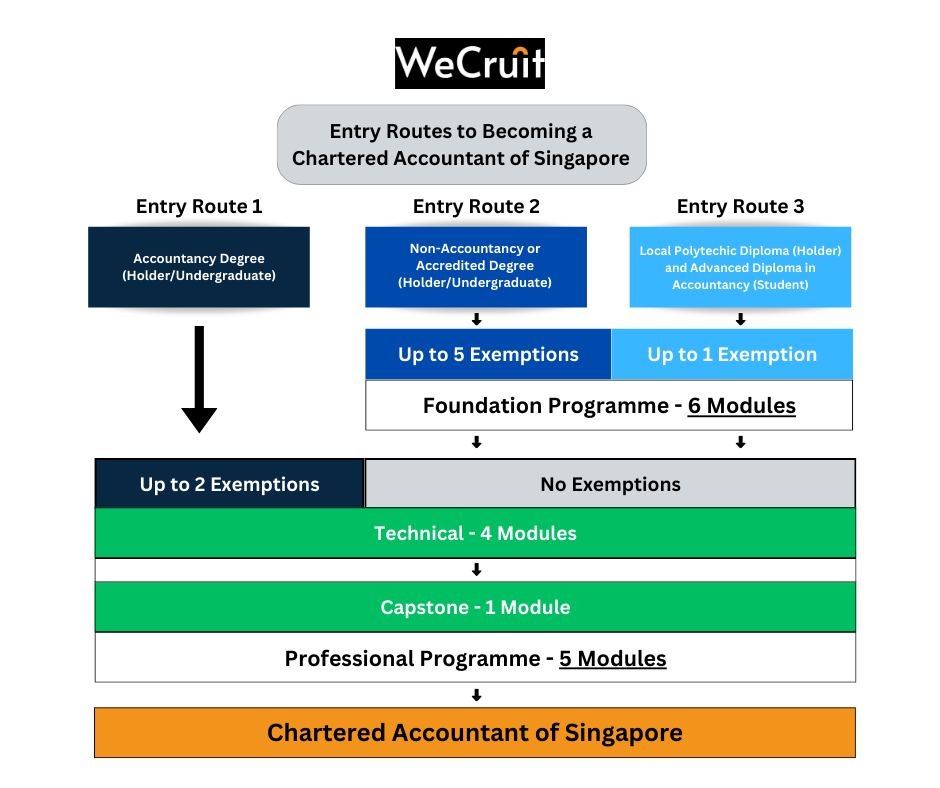
There are three main pathways to enter the Singapore Chartered Accountant Qualification (SCAQ), depending on your academic background and professional credentials. Each route determines whether you start with the Foundation Programme (6 papers) or the Professional Programme (4 papers + 1 capstone module).
If you are pursuing or have completed an accountancy degree from a recognised local university (NUS, NTU, SIT, SMU, SUSS):
✅ Apply for the Professional Programme
✅ Check for exemptions from Financial Reporting (FR) and Taxation (TX) modules
If your degree is from a non-autonomous university, check if it’s in the Accredited or Recognised Degree Listing:
If your degree is in a field other than accountancy, check if it’s in the Accredited or Recognised Degree Listing:
If you hold an Accountancy Diploma from Ngee Ann Polytechnic (NP), Singapore Polytechnic (SP), Nanyang Polytechnic (NYP), or Temasek Polytechnic (TP):
✅ Apply for Ngee Ann Polytechnic’s Advanced Diploma in Accountancy
OR
✅ Apply for the Foundation Programme and check for module exemptions
If your diploma is not in accountancy: Apply for the Foundation Programme.
If you are a full member of any of the following professional bodies:
✅ CA ANZ, CAI, ICAEW, ICAS → Apply for CA (Singapore) via Reciprocal Membership Agreements
If you are a full member of:
✅ HKICPA, Tax Academy Singapore, ISCA PE, ACCA
Yes? → Apply for the Foundation Programme and check for module exemptions
If you are a CPA Australia member:
✅ Apply for CA (Singapore) via Mutual Recognition Agreement through:
Route 1: Transitional arrangement route
Route 2: Normal training route
Once eligible, you can apply for the Professional Programme and check for module exemptions.
Understanding the earning potential in the accounting profession is crucial for aspiring accountants and those considering a career in this field. In Singapore, accountant salaries vary based on factors such as experience, qualifications, and specific roles within the industry.
Entry-Level Accountants: Fresh graduates entering the accounting profession can expect a median starting salary of approximately SGD 3,600 per month. This figure varies slightly depending on the university attended and the specific degree obtained. For instance:
Experienced Accountants: With several years of experience, accountants see a significant increase in their earnings. According to data:
Several factors influence an accountant’s salary in Singapore:
The accounting profession in Singapore offers a rewarding career path with competitive salaries that grow with experience, qualifications, and specialisation. Aspiring accountants should consider pursuing relevant certifications and gaining experience in sectors that align with their career goals to maximise their earning potential.
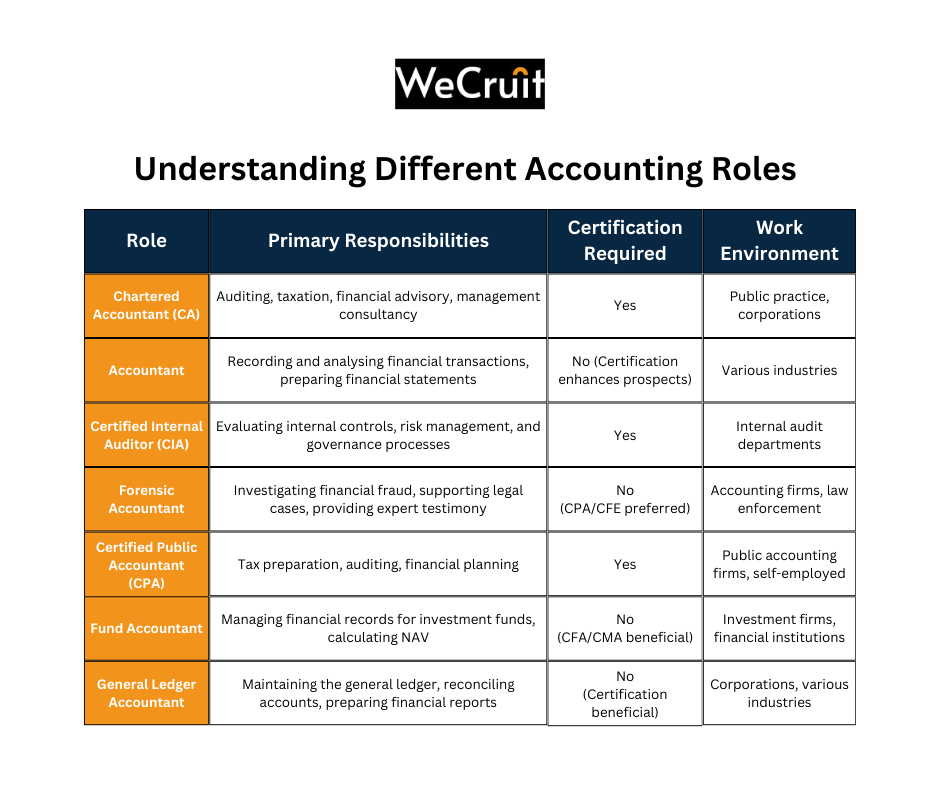
The accounting profession encompasses various roles, each with distinct responsibilities and qualifications. Below is an overview of several key positions:
A Chartered Accountant (CA) is a professional accountant who has obtained certification from a recognised chartered accountancy body. CAs are qualified to perform a range of accounting services, including auditing financial statements, taxation, financial advising, and management consultancy. They adhere to strict professional standards and are often required to engage in continuous professional development.
An Accountant is a professional responsible for recording, analysing, and reporting financial transactions for individuals, businesses, or organisations. Their duties may include preparing financial statements, managing budgets, performing audits, and ensuring compliance with financial regulations. Accountants can specialise in various fields such as management accounting, tax accounting, and financial accounting.
A Certified Internal Auditor (CIA) is a certification granted to accountants who specialise in internal auditing. CIAs assess an organisation’s internal controls, risk management, and governance processes to ensure efficiency and compliance. This designation is recognised globally and is awarded by the Institute of Internal Auditors (IIA).
A Forensic Accountant utilises accounting, auditing, and investigative skills to examine financial records for signs of fraud, embezzlement, or other financial misconduct. They often work closely with law enforcement agencies and may provide expert testimony during legal proceedings. Their work involves detailed analysis to uncover discrepancies and support litigation cases.
A Certified Public Accountant (CPA) is a licensed professional who has passed the Uniform CPA Examination and met additional state certification and experience requirements. CPAs offer a wide range of accounting services, including tax preparation, auditing, and financial planning.
In contrast, a Forensic Accountant focuses specifically on investigating financial discrepancies and fraud. While many forensic accountants hold CPA credentials, their specialised work involves legal proceedings and investigative practices beyond the typical scope of a CPA’s duties.
A Fund Accountant manages and oversees financial reports and records for investment funds, such as mutual funds or hedge funds. Their responsibilities include tracking the fund’s performance, calculating net asset values (NAV), ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements, and preparing financial statements for investors.
A General Ledger Accountant is responsible for maintaining and managing the general ledger, which is the central repository for an organisation’s financial data. Their tasks include recording all financial transactions, reconciling accounts, ensuring accuracy of financial data, and assisting in the preparation of financial statements.
Quickly compare key accounting roles at a glance with this easy-to-read table, summarising responsibilities, qualifications, and work environment insights.
An accountant plays a pivotal role in enhancing your business’s financial health and operational efficiency. Here’s how an accountant can help your business:
Accountants provide critical insights into your financial status, aiding in informed decision-making and strategic planning. They analyse cash flow patterns, manage budgets, and forecast financial trends, ensuring your business remains on a path to growth and profitability.
Navigating the complexities of tax regulations can be challenging. Accountants ensure your business complies with all tax laws, accurately preparing returns and identifying deductions and credits to minimise tax liabilities. This proactive approach not only ensures compliance but also optimises your tax position.
By handling financial record-keeping and administrative tasks, accountants free up your time, allowing you to focus on core business activities. This delegation enhances productivity and ensures that financial tasks are managed efficiently and accurately.
Accountants implement robust internal controls to safeguard your business assets. They monitor financial transactions for irregularities, helping to prevent fraud and ensuring the integrity of your financial data.
With their expertise in financial reporting and analysis, accountants can prepare compelling financial statements and business plans that attract investors and lenders, facilitating access to necessary capital for expansion and growth.
Finding the right accounting professionals is crucial for your business’s success. WeCruit specialises in connecting businesses with top-tier accounting talent, ensuring a perfect match for your specific needs. Whether you’re seeking entry-level accountants or experienced CFOs, WeCruit’s extensive network and industry expertise make the recruitment process seamless and efficient.
Reach out to our expert recruiters at WeCruit, you gain access to professionals who can drive financial excellence and contribute significantly to your business’s growth and stability.
To become a Chartered Accountant (CA) in Singapore, you need to:
Upon fulfilling these criteria, you can apply for membership with the Institute of Singapore Chartered Accountants (ISCA) to earn the CA (Singapore) designation.
Accountant salaries in Singapore vary based on experience and qualifications:
A Chartered Accountant (CA) is a highly qualified accounting professional certified by a recognised body, such as ISCA in Singapore. CAs are experts in areas like auditing, taxation, financial management, and business advisory services.
Accountants are responsible for:
They play a crucial role in maintaining the financial health of individuals and organisations.
Forensic accountants specialising in investigating financial fraud can earn significant salaries, especially with extensive experience and specialised skills. While specific figures vary, top-tier forensic accountants in Singapore can earn upwards of SGD 100,000 annually.
Key roles of an accountant include:
Senior accountants in Singapore earn between SGD 73,000 and SGD 94,000 annually, depending on experience and responsibilities.
On average, accountants in Singapore earn about SGD 53,256 annually.
Wecruit Pte Ltd (“Wecruit”) was incorporated with the idea that employment is an intimate process of human interaction.

Contact Us
© 2025 Wecruit. All Rights Reserved.
